RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS - Genome sequence data of Bacillus sp. CCB-MMP212 isolated from Malaysian mangrove: A potential strain in arsenic resistance with ArsI, C•As lyase
by Nor Azura Azami, Nyok-Sean Lau, Go Furusawa
Arsenicis a toxic element found in both industrially contaminated sites and natural environments such as geothermal springs. Activities such as mining, smelting, ore processing, and using arsenic-based pesticides or herbicides lead to arsenic pollution. In natural environments, many bacterial species play an important role in the detoxification of arsenic. Bacillus sp. CCB-MMP212 was isolated from mangrove sediment during the microbial diversity investigation of Matang Mangrove Forest, Perak, Malaysia. Ms. Nor Azura Azami, Dr. Nyok-Sean Lau, and Dr. Go Furusawa determined the complete whole-genome sequence of Bacillus sp. CCB-MMP212 using the Oxford Nanopore and Illumina platforms and investigated genes related to arsenic resistance.
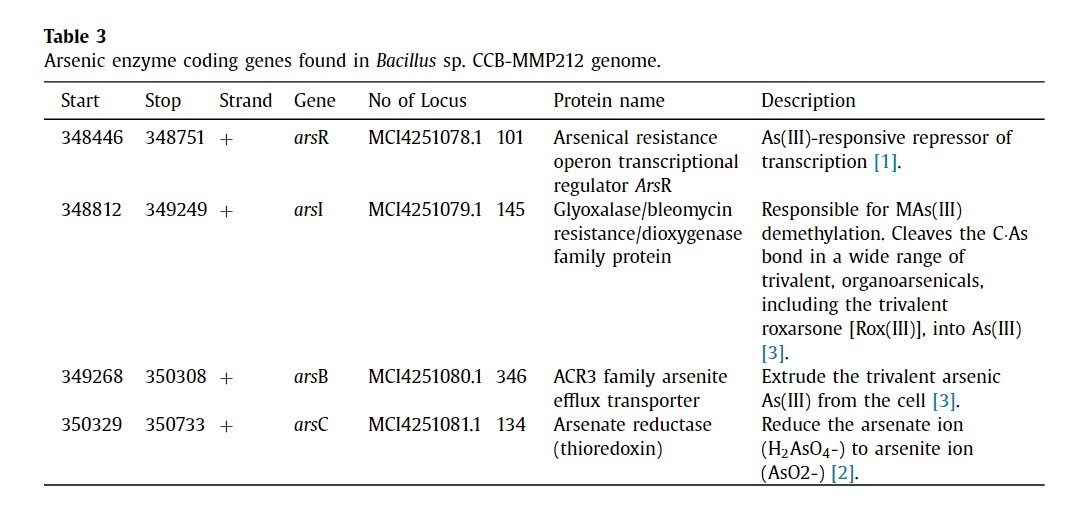
An arsenic resistance (ars) operon consisting of arsenic resistance operon repressor (arsR), ACR3 family arsenite efflux transporter (arsB), and arsenate reductase (arsC) were found in the genome. Interestingly, the arsenic inducible gene (arsI), which encoded a dioxygenase with C•As lyase activity, was also found in the ars operon. The enzyme is crucial for the methylation of methylarsonous acid [MAs(III)] and trivalent roxarsone [Rox(III)]. This dataset reveals the genetic ability of this strain in arsenic resistance. To the best of our knowledge, the arsI encoding C•As lyase is rarely reported within the genus Bacillus. Therefore, the dataset presented in this manuscript provides further insight into the arsenic resistance mechanisms of the genus Bacillus.
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352340922008046
CCB Ref.: 2202_RH_naa_02
Date : 30/12/2022
- Hits: 1042