RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS - A novel alginate-degrading bacterium, Saccharobesus litoralis: a novel genus of the family Alteromonadaceae.
by Rosyada Amran Amrina , Go Furusawa , Nyok-Sean Lau
Earth may contain 1011 to 1012 species of microbes, and 99.999 percent of them have yet to be discovered and identified. Of course, many bacterial species in the marine ecosystem are yet identified. In 2016, we isolated an alginate-degrading bacterium, CCB-QB4T, from a coastal area of Penang, Malaysia. Ms. Rosyada Amrina and Dr. Nyok-Sean Lau, under the supervision of Dr. Go Furusawa, identified the strain using phenotypic, chemotaxonomic, and phylogenetic approaches.
Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain CCB-QB4T showed 94.07, 92.69, 91.52, and 90.90 % sequence similarity to Algibacillus agarilyticus RQJ05T, Catenovulum maritimum Q1T, C. agarivorans YM01T, and C. sediminis D2T, respectively. The low sequence similarity indicated that CCB-QB4T does not belong to these genera. Average nucleotide identity (ANI), the average amino acid identity (AAI), and the digital DNA–DNA hybridization (dDDH) values of CCB-QB4T against four test strains are well below the species threshold values, indicating that CCB-QB4T is classified in a novel genus. Interestingly, although A. agarilyticus RQJ05T, which is the closest species of CCB-QB4T, did not require any carbon sources for its cell growth, the addition of carbon sources was mandatory for the cell growth of CCB-QB4T. The major cellular fatty acid composition of CCB-QB4T was not similar to that of A. agarilyticus RQJ05T. These results demonstrated that strain CCB-QB4T represents a novel species in a new genus of the family Alteromonadaceae, for which the name Saccharobesus litoralis gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed.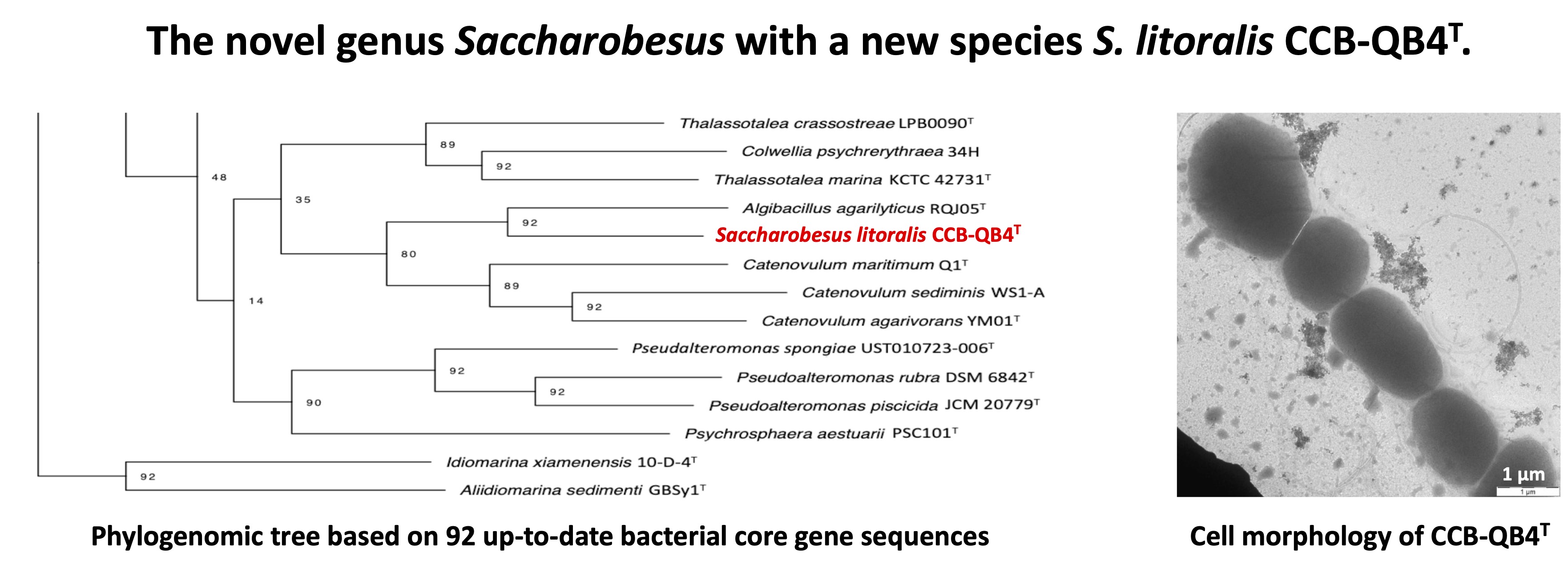
Link: DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.005087
CCB Ref.: 2022_RH_gf_02
Date: 18/10/2022
- Hits: 1811