Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer synthesis by using 1-pentanol and oleic acid: Process optimization and polymer characterization
by K. Shantini · N.A. Azami · H. Kai-Hee · A.R.M. Yahya · A.A. Amirul*
(2021). Journal of Polymer Research. Volume 28, Article number: 247
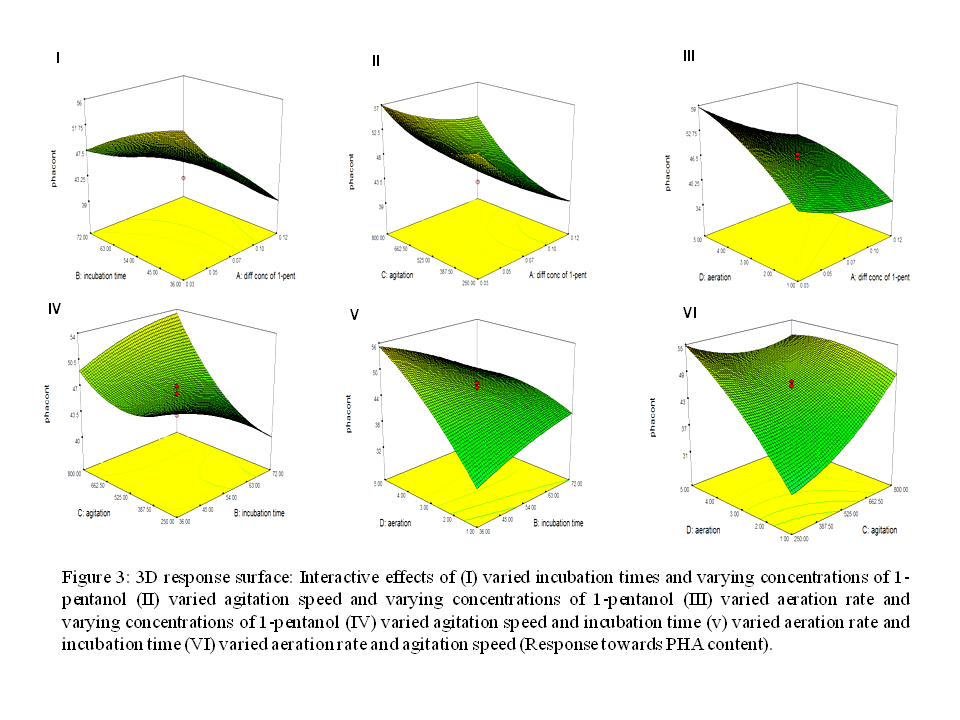
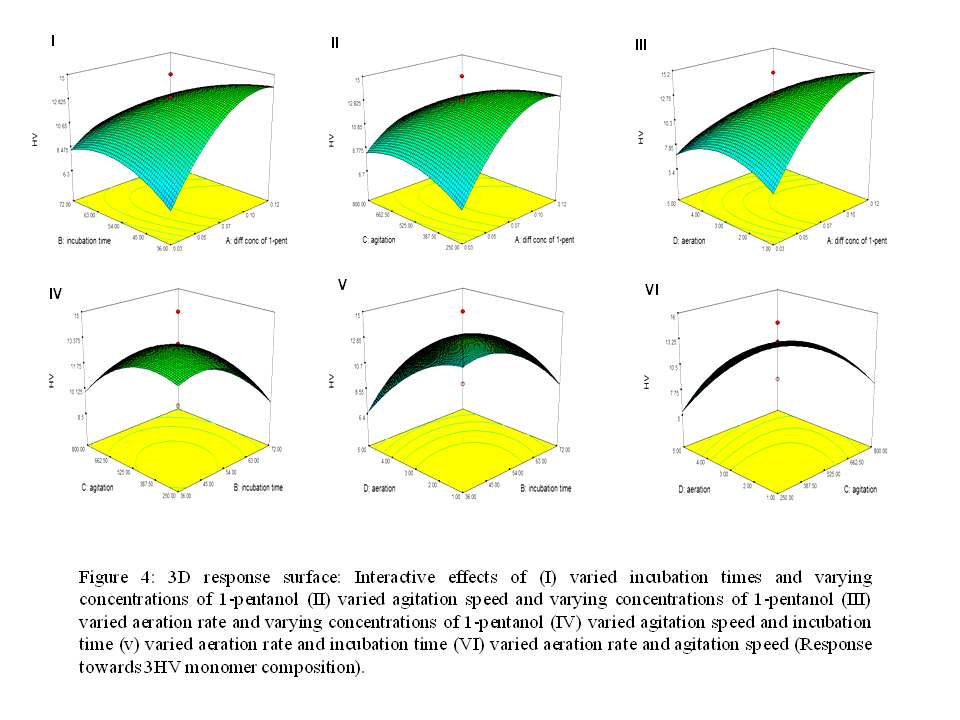
One major discovery in producing eco-friendly bioplastic is polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). These polymers are used by bacteria as an alternative source of fatty acids that are metabolized under stressed conditions. Although PHAs hold a bright future, there were major challenges to commercialize the PHAs. These include the high production cost of this biodegradable material due to the high energy demand for super-hot steam sterilization and intensive pressure aeration, slow growth of microorganisms, discontinuous production processes, and complicated downstream processing. Therefore, many strategies are being examined to overcome the production costs of this copolymer for a sustainable production process. The present study was intended to optimize and increase the productivity of copolymer by using statistical design. The novelty of this work came from the strategies on the optimization of copolymer using 1-pentanol and oleic acid for the production of copolymer P(3HB-co-3HV). Investigations were carried out in a 3.6-L bioreactor by considering critical factors such as aeration and agitation rates. A novel strain, Cupriavidus malaysiensis sp. USMAA2-4 was used to produce this copolymer. This has helped to overcome the production cost and improve the mechanical properties of the copolymers.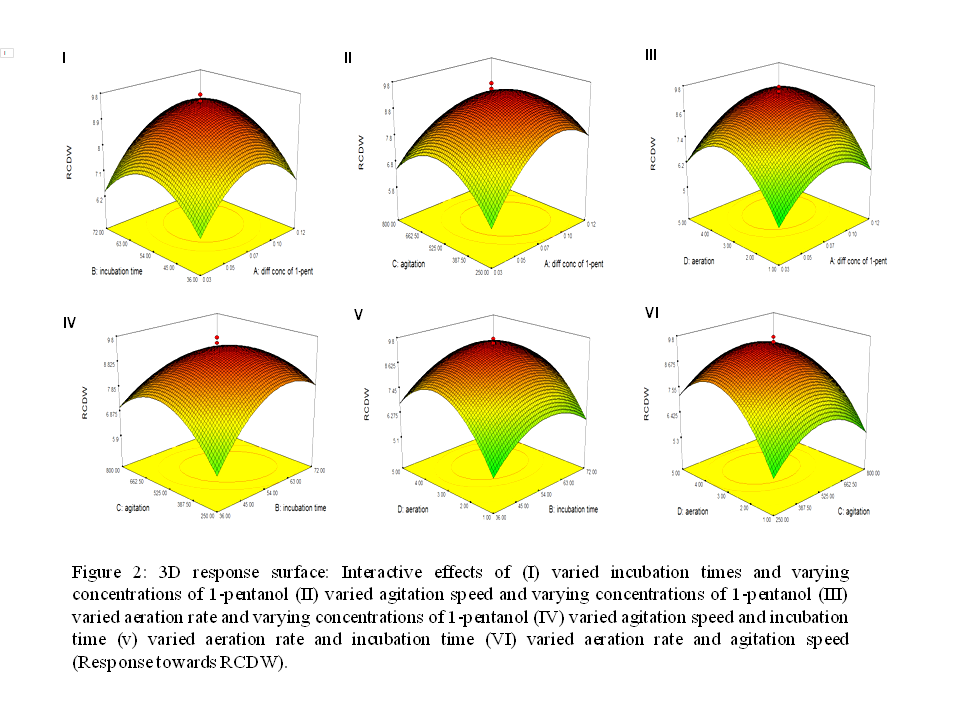
Full Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10965-021-02608-9
CCB Ref: 2021_RH_2_naa
Date: 16/06/2021
- Hits: 1586