Purification and characterization of new bio-plastic degrading enzyme from Burkholderia cepacia DP1
by Nor Azura Azamib, Wirjon Ira Aryanib, Teh Aik-Hongb, A.A. Amirula,b,c
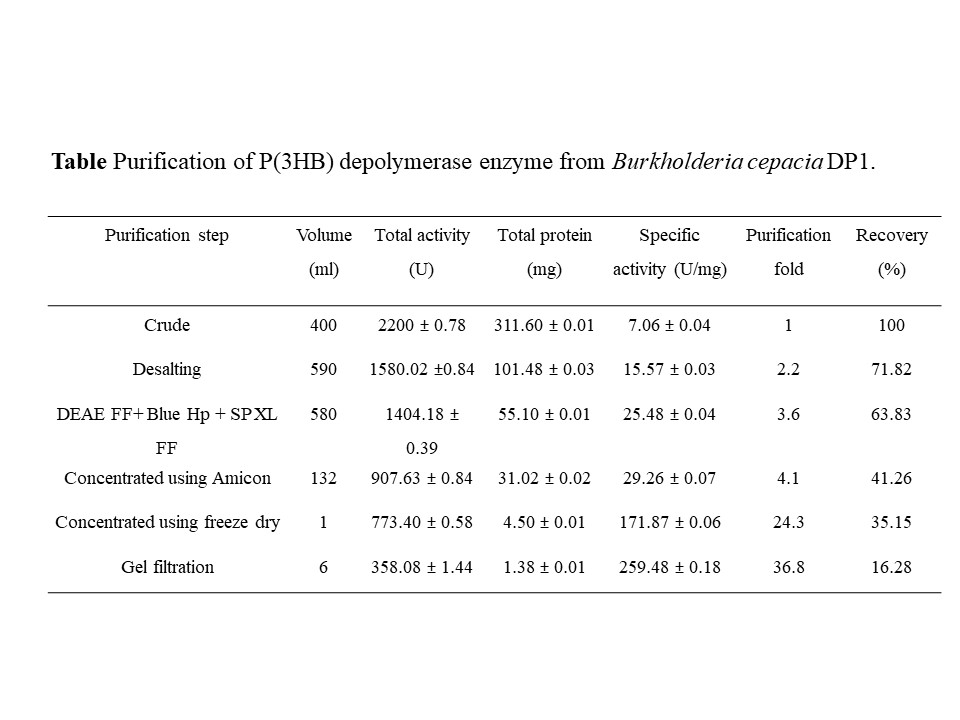
Over the past decades, PHAs have gained industrial interest because of their biodegradability and biocompatibility. Depolymerase is an enzyme that plays an important role in the hydrolysis of PHAs. P(3HB) depolymerases are carboxyesterases that can degrade the PHAs either extracellularly or intracellularly. Extracellular depolymerase enzymes are secreted by various microorganisms in the environment such as soil, sludge, and freshwater. In this manuscript, we report the purification and characterization of the bio-plastic degrading enzyme by Burkholderia cepacia DP1 isolated from soil in Penang, Malaysia. The novelty of this work comes from the ability of this isolate in producing a depolymerase enzyme that efficiently degrades biodegradable plastic in a green and eco-friendly approach. Bio-plastic degrading bacteria from the genus Burkholderia were rarely reported. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report that demonstrated the purification and biochemical characteristics of the P(3HB) depolymerase enzyme from the genus Burkholderia. This finding might contribute as a significant addition to the scientific literature on the purification process and characterization of the bio-plastic degrading enzyme.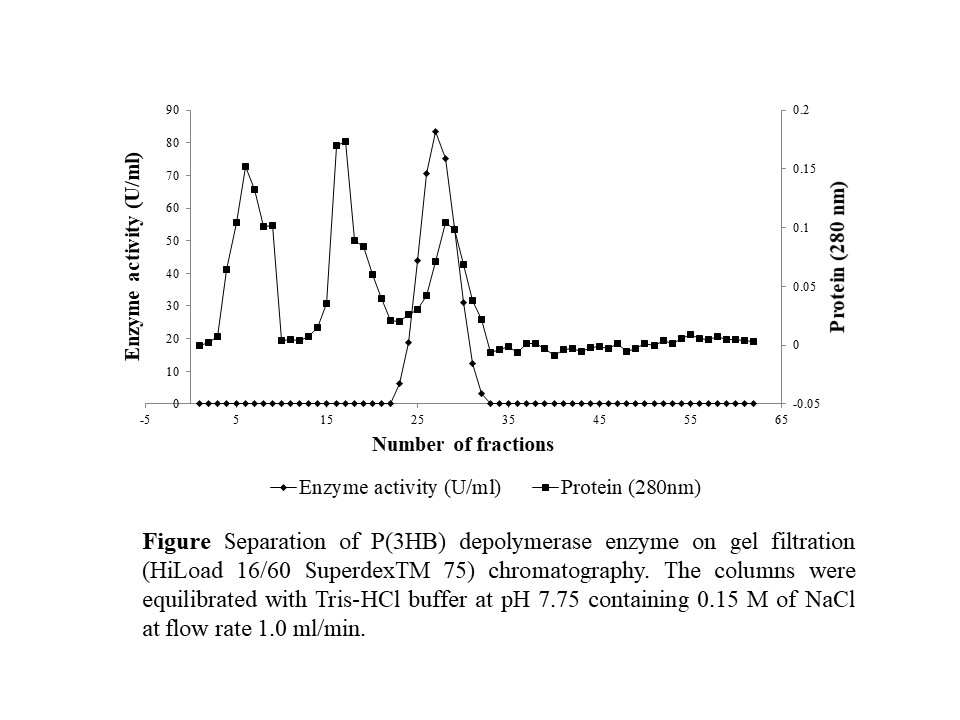
Full Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S104659281830384X
CCB Ref: 2021_RH_1_naa
Date: 19/04/2021
- Hits: 344